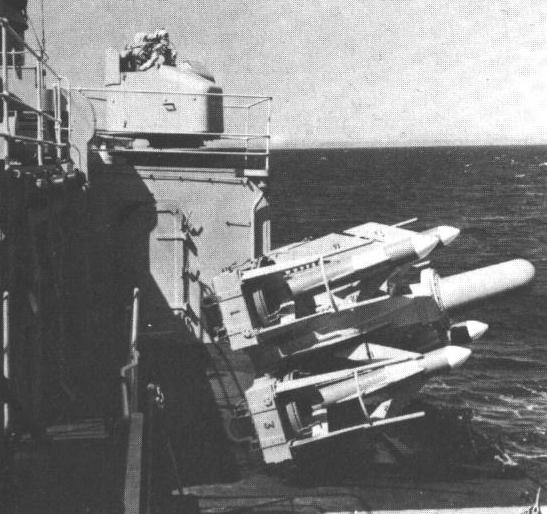

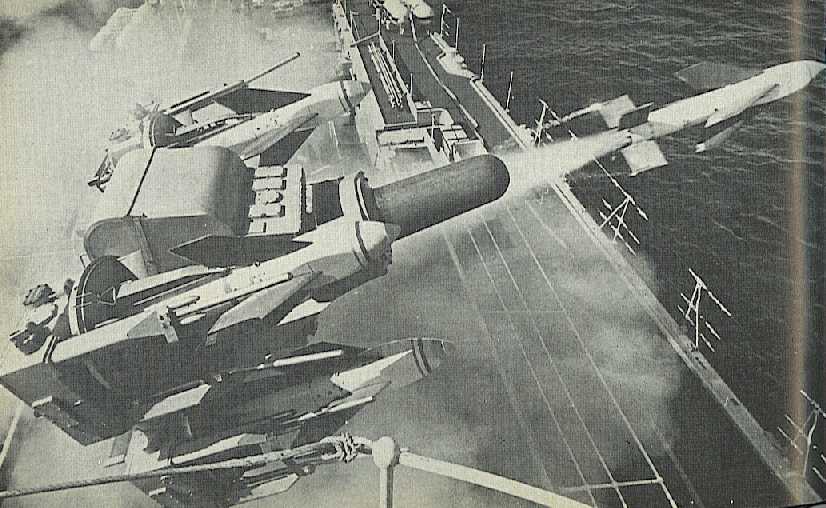
Sea Cat was the first point-defense missile to enter Naval service and was based upon the Malkara anti-tank missile. This missile was designed to replace twin 40 mm Bofors mounts with a quad-missile launcher. The earliest version, GWS-20, was eyeball controlled, with the operator using binoculars and a joystick.
To aid in the replacement of the 40 mm mountings, the GWS-21 version was actually controlled by the Type 262 Radar gun control used by the 40 mm Bofors. GWS-22 uses a modified director based upon the MRS-3 (the British version of the Mark 56 FCS). GWS-24 employs the WSA-4 FCS.
Sea Cat is mounted on a 4 round trainable launcher. Reloading is by hand, carrying missiles by trolley from the magazine. There was also a lightweight 3 round version for small ships.
The missile proved accurate, reliable and cheap and 7 other countries have used it, although it has been replaced in Royal Navy service by the Sea Dart and Sea Wolf.
| Designation | Sea Cat GSW-20, 21, 22 and 24 |
|---|---|
| Ship Class Used On | Tribal Class (GWS-21) Country and Leander Classes (GWS-22) Amazon Class (GWS-24) |
| Date In Service | 1962 |
| Weight | 150 lbs. (68 kg) |
| Dimensions | 48.3 x 378.5 in (19 x 149 cm) Span: 165 in (65 cm) |
| Payload | Warhead has both proximity and impact fuzing |
| Speed / Range | Mach 0.9 / 5,500 yards (5,000 m) |
| Propulsion | Dual thrust solid fuel |
Data from:
- "Jane's Pocket Book 9: Naval Armament" edited by Denis Archer
- "The Naval Institute Guide to World Naval Weapon Systems 1991/92" by Norman Friedman
