| Ship Class Used On | Small surface ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | Started in 1870 |
| Date In Service | 1895 |
| Weight | 580 lbs. (263 kg) |
| Overall Length | 132 in (3.353 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 100 lbs. (45.4 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 200 yards (180 m) at 24 knots, then slower out to a maximum of 800 yards (730 m) |
| Power | 131 lbs. (59 kg) steel flywheel spun up to 10,000 rpm |
| Guidance | Pendulum operated rudder for anti-roll, directional stability and depth control |
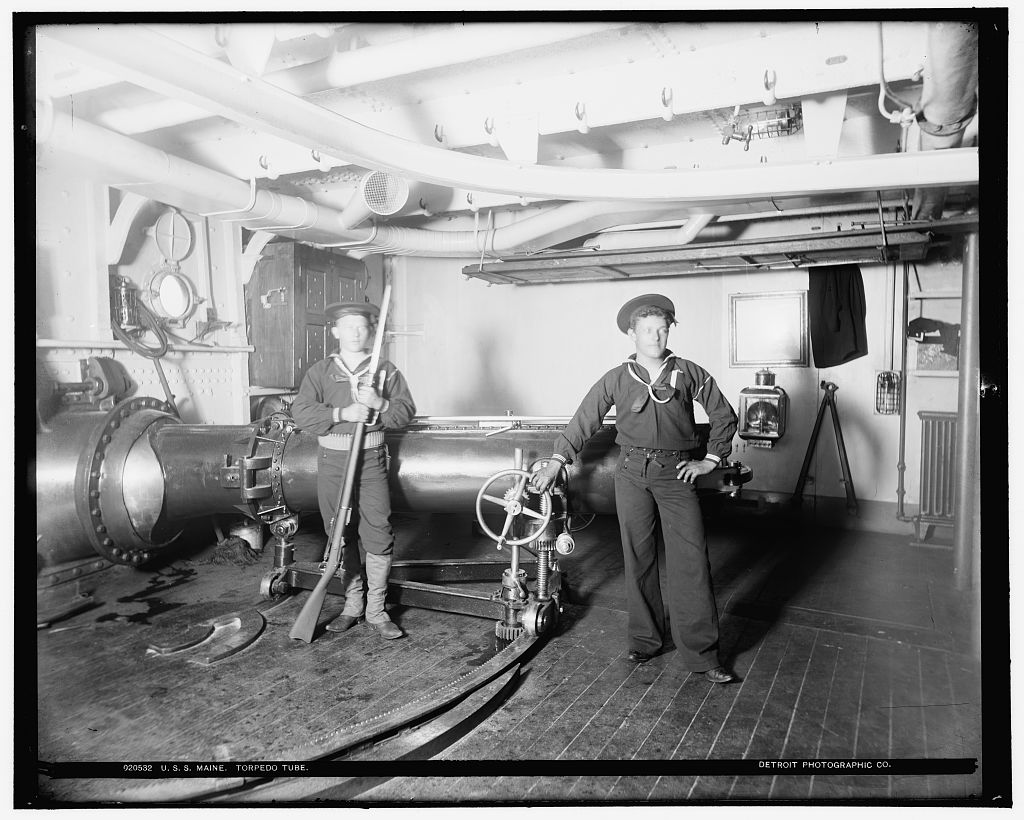
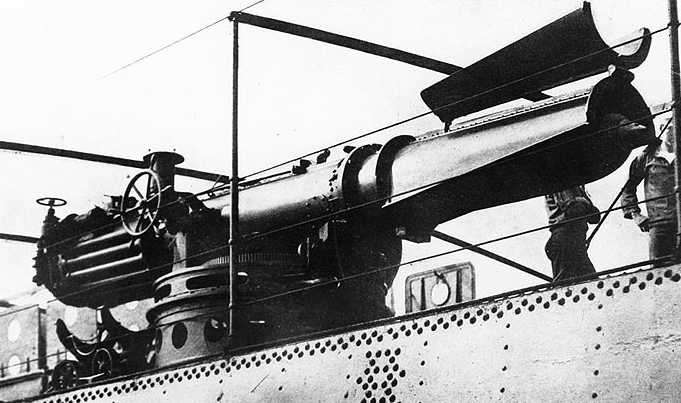
The first USA torpedo, it was smaller and cheaper than the British Whitehead and required no air flask, a difficult thing for the USA to manufacture at the time. As it was flywheel powered, this torpedo did not leave a wake and could steer a straighter course than the Whitehead as its flywheel acted as a gyroscope. The flywheel was spun up by a small steam turbine mounted on the torpedo tube and drove two shafted propellers. The propellars were variable pitch and were designed to maintain a constant forward speed as the flywheel slowed. Thirty torpedoes were ordered in 1889 with twenty more being ordered in 1894. Placed in service in 1895 and removed in 1903. Difficulties and delays in production led the Navy to investigate the Whitehead torpedoes.
| Ship Class Used On | Surface Ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | about 1888 |
| Date In Service | 1894 |
| Weight | 845 lbs. (383 kg) |
| Overall Length | 140 in (3.556 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 118 lbs. (53.5 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 800 yards (730 m) / 26 knots |
| Power | Air-flask (cold running) compressed air powered, three cylinder, radial Brotherhood pattern engines. |
| Guidance | Preset Rudder adjustment, had poor directional stability with a contractual requirement for horizontal deviation of no more than +/- 24 yards (22 m) at 800 yards (730 m) |
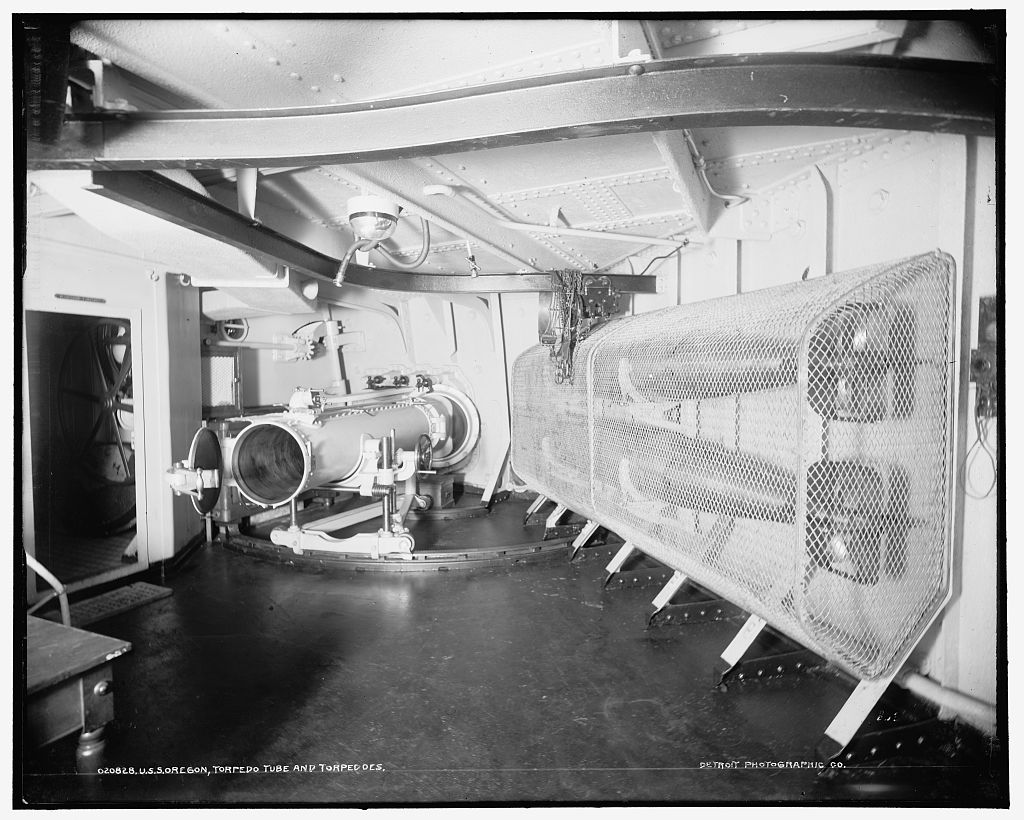
The US Navy negotiated for the Whitehead torpedo patent rights with a license to build torpedoes in the USA being granted in 1891. The Navy awarded a contract to the E.W. Bliss company on 19 May 1891 for 100 torpedoes to an improved Whitehead design. Compared to the Howell, they were much better depth-keepers but less accurate.
Somewhat confusingly, the Whitehead Mark 1 and Mark 2 torpedoes were built both in a 3.55 m (140 inch) version and in a 5.0 m (197 inch) version. The shorter ones were known as the "3.55 m x 45 cm Whitehead" torpedoes while the longer ones were known as the "5.0 m x 45 cm Whitehead" torpedoes. The Whitehead Mark 3 was built only in a 3.55 m (140 inch) version. The longer torpedoes and the Mark 3 were redesigned with letter codes in 1913, as described below.
| Ship Class Used On | Surface Ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | 1896 |
| Date In Service | 1898 |
| Weight | 1,160 lbs. (526 kg) |
| Overall Length | 197 in (5.004 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 220 lbs. (100 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 1,000 yards (910 m) / 27.5 knots |
| Power | Air-flask (cold running) compressed air powered, three cylinder, radial Brotherhood pattern engines. |
| Guidance
(see Note) |
Early production: Preset Rudder adjustment, had poor directional stability with a contractual requirement
for horizontal deviation of no more than +/- 24 yards (22 m) at 800 yards (730 m)
Later production: Mark 1 Mod 1 gyro |
Manufactured by Bliss, these were a longer version of the basic design. Also known as the "5.0 m x 45 cm Whitehead" when first manufactured, it was designated as the "Type B" in 1913. After tests with the Whitehead Mark 3 torpedo (described below), the last forty of these "Long" Mark 1 torpedoes were given a gyro which had been patented by Ludwig Obry in 1896. This improved the horizontal deviation by 300 percent compared to the earlier Mark 1 torpedoes to +/- 8 yards (7 m) at 800 yards (730 m). However, this gyro proved very hard to maintain.
| Ship Class Used On | Surface Ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | 1895 |
| Date In Service | 1896 |
| Weight | 845 lbs. (383 kg) |
| Overall Length | 140 in (3.556 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 118 lbs. (53.5 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 800 yards (730 m) / 28 knots |
| Power | Air-flask (cold running) compressed air powered, three cylinder, radial Brotherhood pattern engines. |
| Guidance | Preset Rudder adjustment, had poor directional stability with a contractual requirement for horizontal deviation of no more than +/- 24 yards (22 m) at 800 yards (730 m) |
Minor improvement of the Whitehead Mark 1.
| Ship Class Used On | Surface Ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | about 1896 |
| Date In Service | about 1898 |
| Weight | 1,232 lbs. (559 kg) |
| Overall Length | 197 in (5.004 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 132 lbs. (60 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 1,500 yards (1,370 m) / 28.5 knots |
| Power | Air-flask (cold running) compressed air powered, three cylinder, radial Brotherhood pattern engines. |
| Guidance | Mark 1 Mod 1 gyro |
| Ship Class Used On | Surface Ships and Submarines |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | about 1898 |
| Date In Service | about 1900 |
| Weight | 845 lbs. (383 kg) |
| Overall Length | 140 in (3.556 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 118 lbs. (53.5 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 800 yards (730 m) / 27.5 knots |
| Power | Air-flask (cold running) compressed air powered, three cylinder, radial Brotherhood pattern engines. |
| Guidance | Mark 1 Mod 1 gyro |
This was the first US torpedo to be equipped with a gyro which greatly improved accuracy, otherwise it was a minor improvement of the Whitehead Mark 2.
The A through D class submarines originally fired this torpedo, but the C and D classes were modified around 1912 to use any of the longer, more powerful 204 inch (5.2 m) torpedoes.
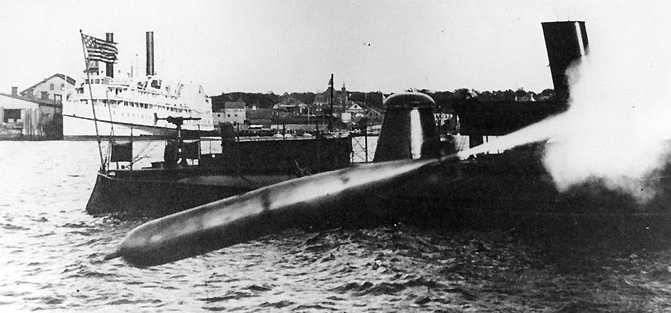

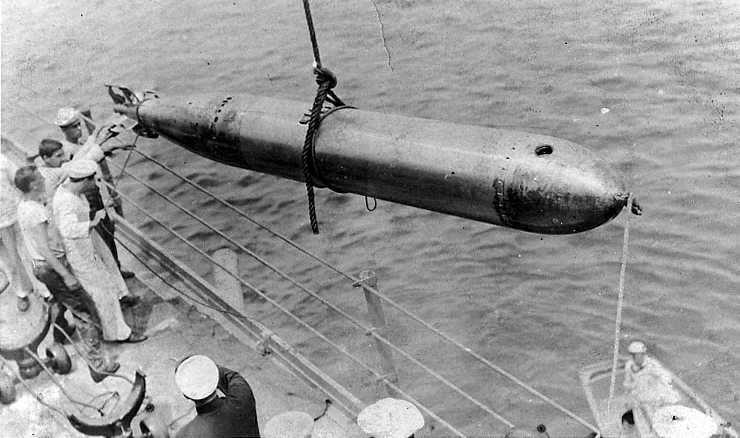
| Ship Class Used On | Surface Ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | 1900 |
| Date In Service | Mod 1: 1904
Mod 2: 1905 |
| Weight | 1,500 lbs. (680 kg) |
| Overall Length | 197 in (5.004 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 200 lbs. (91 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | Mod 1: 4,000 yards (3,660 m) / 27 knots
Mod 2: 4,000 yards (3,660 m) / 26.5 knots |
| Power | Single stage turbine engine, alcohol fired dry heater |
| Guidance | Mod 1: Unknown
Mod 2: Mark 2 Mod 2 gyro |
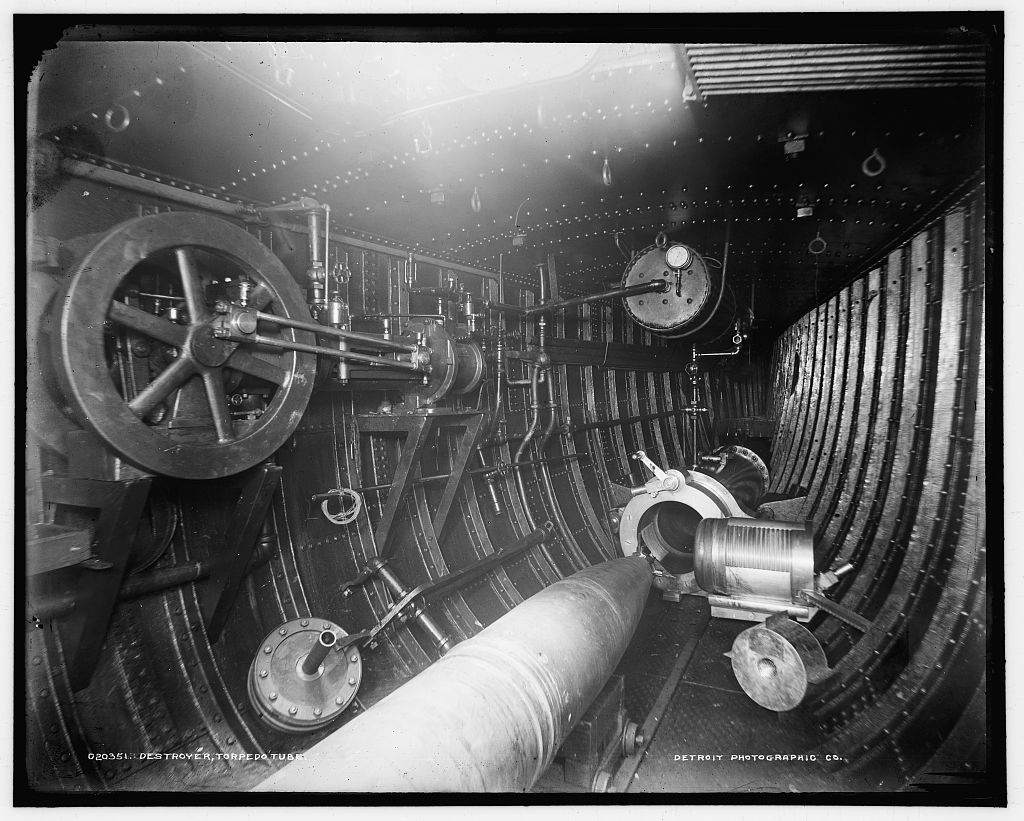
F.M. Leavitt was a Bliss engineer. This design was a substantially improved torpedo, the first to use air heating which gave it much greater range than the compressed cold-air powered Whitehead. This new torpedo had a two stage, single wheel turbine set perpendicular to the propeller shaft to in an attempt to avoid torque problems, but the design still produced an unbalanced torque and unwanted gyroscopic effects. These tended to make the torpedo roll. Used a single 4-blade propeller.
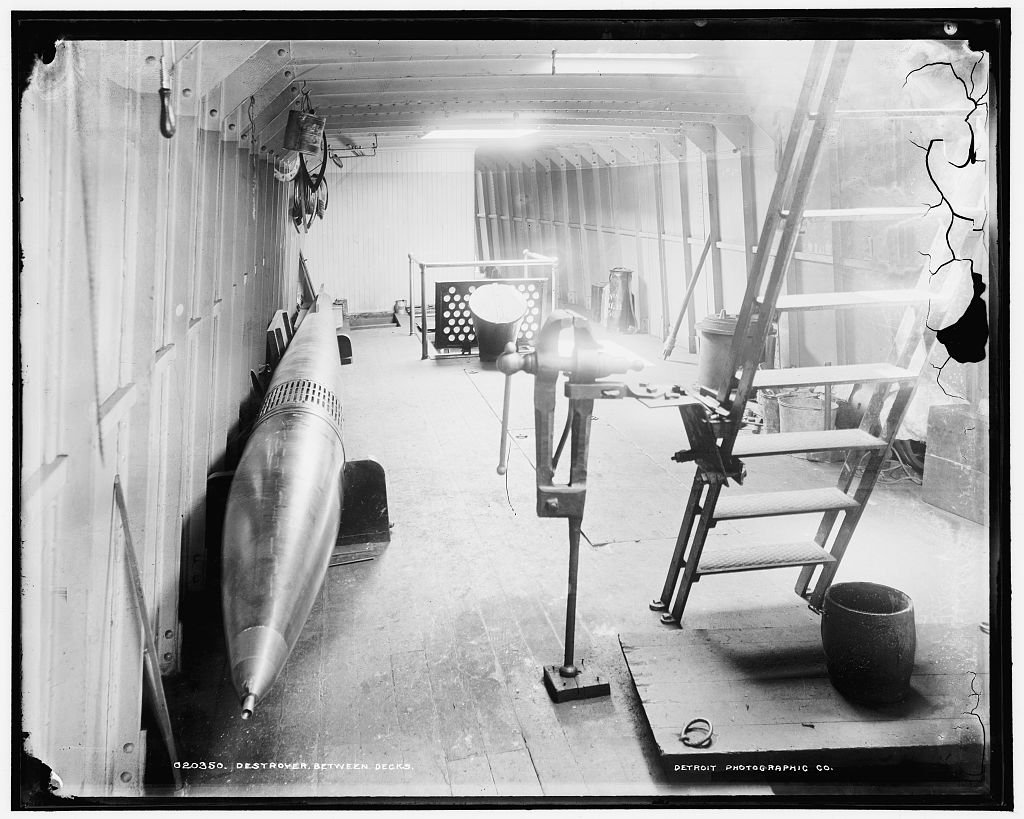
The original Bliss-Leavitt Mark 1 was an experimental torpedo with two built in 1903 but not issued to the fleet. 200 more were ordered on 4 November 1905. Fifty additional torpedoes of the Mod 1 improved design were ordered on the same date. By 1912 all Mark 1 and Mark 1 Mod 1 torpedoes had been converted to the Bliss-Leavitt Mark 1 Mod 2 standard (no details available) and then redesignated as Torpedo Mark 1 in 1913.
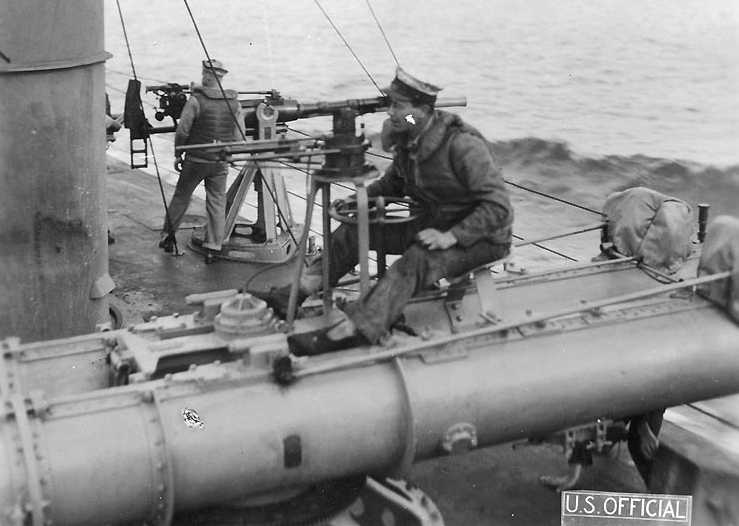

| Ship Class Used On | Surface Ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | about 1904 |
| Date In Service | 1905 |
| Weight | 1,900 lbs. (862 kg) |
| Overall Length | 197 in (5.004 m) |
| Explosive Charge | Mod 0: 207 lbs. (94 kg) wet gun-cotton
Mod 1: 183 lbs. (83 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 3,500 yards (3,200 m) / 26 knots |
| Power | Two-stage turbine engine, alcohol fired dry heaters |
| Guidance | Mark 5 gyro |
Introduced two countra-rotating turbine wheels which drove contra-rotating propellers to overcome the unbalanced torque of the Mark 1. This propulsion system eliminated the rolling problem at a slight cost in range and speed. This propulsion arrangement was used on all subsequent USA torpedoes until after World War II. Designated as Torpedo Mark 2 in 1913.
| Ship Class Used On | Surface Ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | about 1909 |
| Date In Service | about 1910 |
| Weight | 1,500 lbs. (680 kg) |
| Overall Length | 197 in (5.004 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 218 lbs. (99 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 4,000 yards (3,660 m) / 26 knots |
| Power | Turbine engine, alcohol fired dry heaters |
| Guidance | Mark 5 Mod 2 gyro |
Basically a Bliss-Leavitt Mark 2 with increased range. 208 ordered in 1909 and 1910. Designated as Torpedo Mark 3 in 1913.
| Ship Class Used On | Submarines |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | about 1910 |
| Date In Service | about 1912 |
| Weight | 1,547 lbs. (702 kg) |
| Overall Length | 197 in (5.004 m) |
| Explosive Charge | Mod 0: 200 lbs. (91 kg) wet gun-cotton
Mod 1: 199 lbs. (90 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | Mod 0: 2,000 yards (1,830 m) / 30 knots
Mod 1: 3,000 yards (2,740 m) / 29 knots |
| Power | Turbine engine, alcohol fired dry heaters |
| Guidance | Mod 0: Mark 4 Mod 3 gyro
Mod 1: Mark 2 Mod 2 gyro |
First USA torpedo designed specifically for submarines. Twenty-one inch (53.3 cm) torpedoes were too heavy and too bulky for the submarines of the time. For that reason, this torpedo was designed as a scaled down version of the Bliss-Leavitt Mark 3. Designated as Torpedo Mark 4 in 1913. Used by C and D class submarines.
| Ship Class Used On | Destroyers, Torpedo Boats and other small ships |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | 1908 |
| Date In Service | about 1910 |
| Weight | 1,452 lbs. (659 kg) |
| Overall Length | 204 in (5.182 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 199 lbs. (90 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 4,000 yards (3,660 m) / 27 knots
2,000 yards (1,830 m) / 36 knots 1,000 yards (910 m) / 40 knots |
| Power | Dry heater system (hot running), four cylinder reciprocating engine |
| Guidance | Mark 1 Mod 3 gyro |
First torpedo in US service that was built by a foreign company. Manufactured by the Whitehead facility in Weymouth, UK. Later, this design was manufactured under license by the US and became the first torpedo built at the Newport Facility. First major improvement to the original Whitehead engine in that a heater was used for the air feed, which increased the range by a factor of five.
This was the first US torpedo that could be set for any one of three speeds. However, the speed had to be set before the torpedo was loaded into the tube, which limited its tactical flexibility.
This was the last piston engine used in USN torpedoes until the Mark 46. Replaced by the Bliss-Leavitt Mark 7.
| Ship Class Used On | Destroyers, Cruisers and E through H class submarines |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | about 1908 |
| Date In Service | about 1911 |
| Weight | 1,800 lbs. (616 kg) |
| Overall Length | 204 in (5.182 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 200 lbs. (90 kg) wet gun-cotton |
| Range / Speed | 2,000 yards (1,830 m) / 35 knots |
| Power | Turbine engine, alcohol fired dry heaters |
| Guidance | Mark 6 gyro |
The Bliss-Leavitt Mark 6 introduced a new turbine configuration in which the wheels were horizontal. This configuration has been the most common choice for USN torpedo turbine systems ever since. 100 were ordered in 1909.
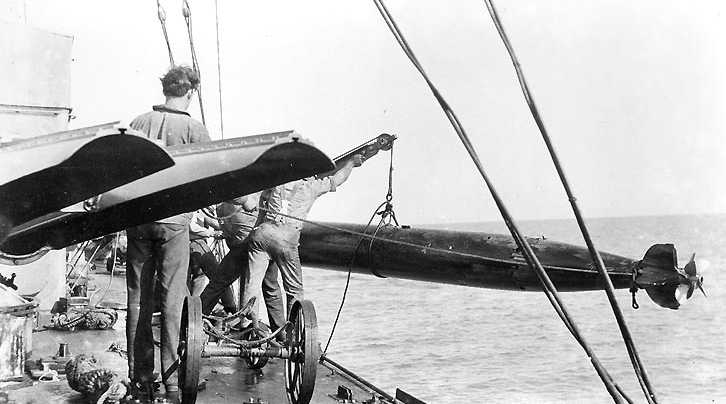
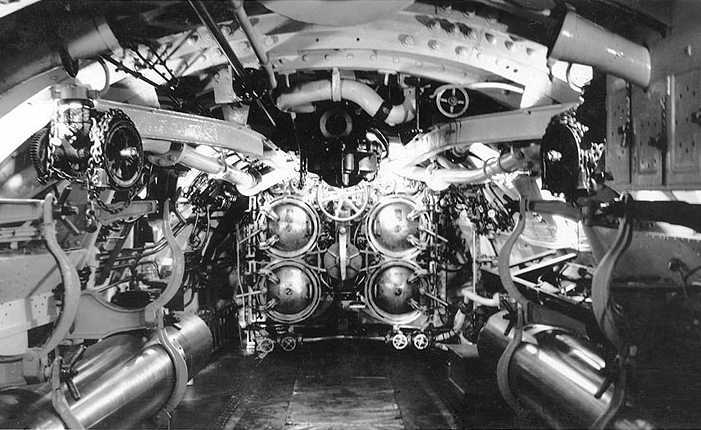


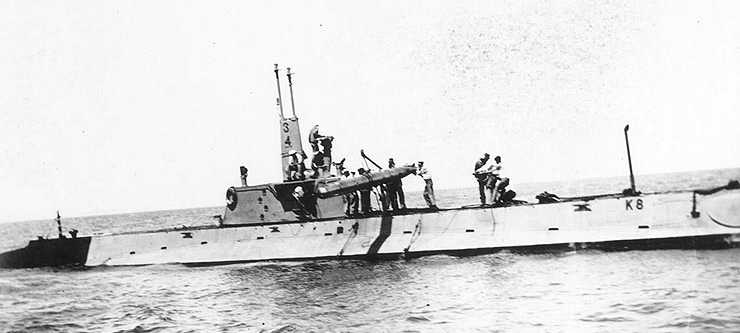
| Ship Class Used On | "K," "O" and "R" Class Submarines |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | 1910 |
| Date In Service | 1912 |
| Weight | Mod 0 (submarines): 1,588 lbs. (720 kg) |
| Overall Length | 204 in (5.182 m) |
| Explosive Charge | Mod 0: 205 lbs. (93 kg) TNT |
| Range / Speed | Mod 0: 4,000 yards (3,650 m) / 32 knots |
| Power | Wet-Heater |
| Guidance | Mark 7 gyro |
First wet-heater (water spray into combustion chamber) torpedo in the US Navy. 240 ordered in 1912. Still being used by old submarines during World War II. Some Mark 7 torpedoes were modified for use by aircraft (see below).
| Ship Class Used On | Submarines
Aircraft |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | About 1916 |
| Date In Service | 1917 |
| Weight | 7D: 1,036 lbs. (470 kg) |
| Overall Length | 120 in (3.048 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 7D: 200 lbs. (90 kg) TNT |
| Range / Speed | 7D: 2,000 yards (1,800 m) / 35 knots |
| Power | Wet-heater |
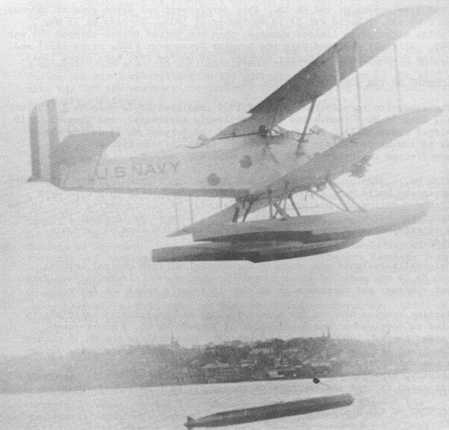
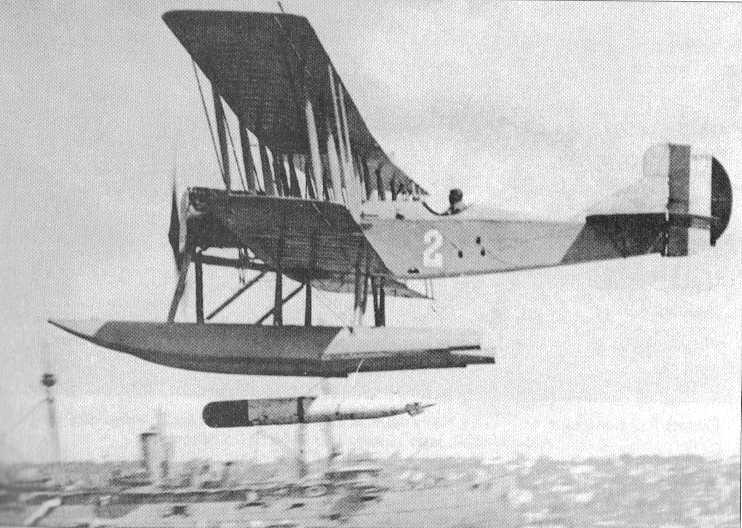
Smaller version of the Mark 7 developed to fit the shorter torpedo tubes on old submarines. Never deployed for that purpose, but used during early aircraft tests. After a series of drops with dummy torpedoes, a live Type D was successfully launched from an R-6L Navy floatplane on 14 July 1919. 43 more Type D torpedoes were launched from planes during the next 12 months.
| Ship Class Used On | Aircraft |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | 1920 |
| Date In Service | 1920 |
| Weight | 7D Mod A: 1,593 lbs. (723 kg)
7D Mod 2A: 1,736 lbs. (787 kg) 7D Mod 5A: 1,628 lbs. (738 kg) |
| Overall Length | 204 in (5.182 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 7D Mod A: 205 lbs. (93 kg) TNT
7D Mod 2A: 319 lbs. (145 kg) TNT 7D Mod 5A: 326 lbs. (148 kg) TNT or TPX |
| Range / Speed | 7D Mod A: 3,200 yards (2,930 m) / 31 knots
7D Mod 2A: 6,000 yards (5,490 m) / 30 knots 7D Mod 5A: 3,500 yards (3,200 m) / 35 knots |
| Power | Wet-Heater |
| Guidance | Mark 7 Mod 2 gyro |
The first experimental USN aircraft drops with Mark 7 torpedoes were made in May 1920 at the Naval Air Station, Anacostia, Maryland, using two Mark 7 Mod 5 torpedoes. Air speed for these drops is believed to have been 50 to 55 knots at altitudes of 18 and 30 feet (5 and 9 m). It was found that the torpedo dropped from 30 feet (9 m) was badly damaged while the one dropped from 18 feet (5 m) was not. Torpedoes were then modified by strengthening them for shock, installation of exploder safety pin and attachment of a nose drogue.
The first mass torpedo practice against a live target was conducted off the Virginia capes on 22 September 1922 by 18 PT aircraft of Torpedo and Bombing Plane Squadron One. The squadron attacked the designated target, Arkansas (BB-33), which was one of a formation of three battleships which were maneuvering while running at full speed. The attack lasted over a 25 minute period during which time the aircraft approached the ships from both sides and released 17 Mark 7 Mod 1 "A" torpedoes at distances of 500 to 1,000 yards (450 to 900 m). Eight hits were made on the designated target. Subsequent analysis emphasized the artificialities which prevented the practice from demonstrating combat capability of either the surface or air units, but the outstanding fact demonstrated was that torpedoes could be successfully launched from aircraft and be made to run straight.
During trials in 1924, Mark 7 torpedoes were successfully launched from DT-2 torpedo planes at an air speed of 95 knots and from an altitude of 32 feet (10 m).
Aircraft torpedoes of this type were eventually replaced by the Mark 13.
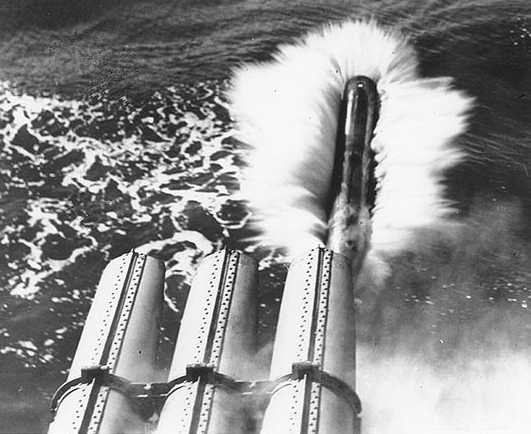
| Ship Class Used On | Flush-deck destroyers |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | About 1914 |
| Date In Service | 1915 |
| Weight | Mods 0, 1, 2, 2A and 2B: 2,761 lbs. (1,252 kg)
Mods 3A, 3B and 3C: 3,050 lbs. (1,383 kg) Mod 8: 3,176 lbs. (1,441 kg) |
| Overall Length | Mods 0, 1, 2, 2A and 2B: 248 in (6.299 m)
Mods 3A, 3B and 3C: 250 in (6.350 m) Mod 8: 256.3 in (6.510 m) |
| Explosive Charge | Mods 0, 1, 2, 2A and 2B: 321 lbs. (146 kg) TNT
Mods 3A, 3B and 3C: 385 lbs. (175 kg) TNT Mod 8: 466 lbs. (211 kg) TNT |
| Range / Speed | Mods 0, 1, 2, 2A and 2B: 10,000 or 12,500 yards (9,140 or 11,430 m) / 27 knots
Mods 3A, 3B and 3C: 13,500 yards (12,340 m) / 27 knots Mod 8: 15,000 yards (13,720 m) / 29 knots |
| Power | Wet-heater |
| Guidance | Most: Mark 8 Mod 1 gyro
Mark 8 Mod 3C: Mark 11 or Mark 11 Mod 1 air sustained gyros |
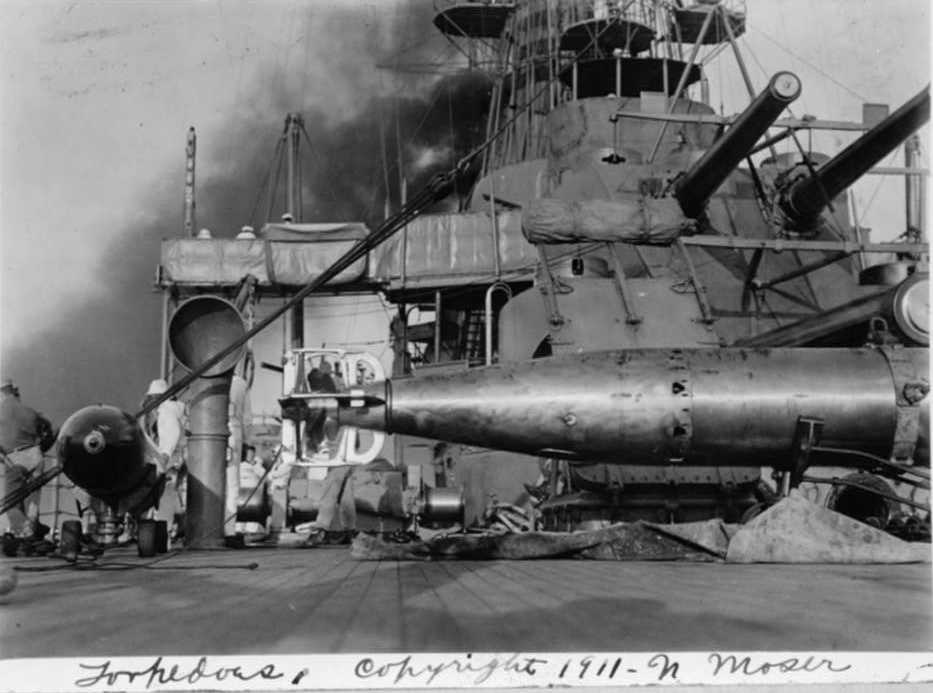
First 21" x 21' (53.3 cm x 6.5 m) USN torpedo. Later versions starting in 1923 - Mod 5, 6 and 8 - had much larger warheads. These torpedoes were still being used on older destroyers and PT boats during World War II. It is possible that a higher speed setting was available for the torpedoes issued to PT boats.
This torpedo was supplied to Britain for use on Lend-Lease Destroyers in 1940. Torpedoes issued to Britain are listed as having a warhead of 380 lbs. (172 kg) TNT and a range of 14,000 yards (12,800 m) at 27 knots.
The Mark 8 Mod 3C differed from Mod 3A and 3B by having air-sustained gyros and a different igniter.
The Mark 8 Mod 3E was an export torpedo supplied at least to Brazil after 1936. It was nearly identical to the Mark 8 Mod 3A.
The Mark 8 torpedoes were later used by PT boats during World War II. These were replaced by the Mark 13 aerial torpedo in mid-1943.
| Ship Class Used On | Mod 1: World War I-era Battleships
Mod 1B: Submarines |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | About 1912 |
| Date In Service | 1915 |
| Weight | Mod 1: 2,059 lbs. (934 kg)
Mod 1B: 2,377 lbs. (1,078 kg) |
| Overall Length | 196 in (5.004 m) |
| Explosive Charge | Mod 1: 210 lbs. (95 kg) TNT
Mod 1B: 395 lbs. (179 kg) Torpex |
| Range / Speed | Mod 1: 9,000 yards (8,230 m) / 27 knots
Mod 1B: 5,500 yards (5,030 m) / 34.5 knots |
| Power | Wet-heater |
| Guidance | Mark 8 Mod 1 gyro |
A short torpedo developed for the submerged tubes on battleships. Originally known as the Bliss-Leavitt Mark 3 Mod 1. Used by "R" and "S" class submarines in World War II. Last torpedo built by Bliss.
| Ship Class Used On | World War I-era Submarines |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | About 1917 |
| Date In Service | About 1918 |
| Weight | Mod 0: 2,050 lbs. (930 kg)
Mod 3: 2,215 lbs. (1,005 kg) |
| Overall Length | 183 in (4.953 m) |
| Explosive Charge | Mod 0: 400 lbs. (181 kg) TNT
Mod 3: 497 lbs. (225 kg) TNT or 485 lbs. (220 kg) Torpex |
| Range / Speed | Mod 0: 5,000 yards (4,570 m) / 30 knots
Mod 3: 3,500 yards (3,200 m) / 36 knots |
| Power | Wet-heater |
| Guidance | Mark 13 Mod 1 gyro |
Last torpedo designed by Bliss and manufactured by the Naval Torpedo Station at Newport. Still used by "S" class submarines during World War II.
| Ship Class Used On | Destroyers and Cruisers |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | About 1924 |
| Date In Service | 1926 |
| Weight | Mod 0: 3,511 lbs. (1,593 kg)
Mod 1: 3,521 lbs. (1,597 kg) |
| Overall Length | 271 in (6.883 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 500 lbs. (227 kg) TNT |
| Range / Speed | 6,000 yards (5,500 m) / 46 knots
10,000 yards (9,150 m) / 34 knots 15,000 yards (13,700 m) / 27 knots |
| Power | Wet-heater |
| Guidance | Mark 12 Mod 1 gyro |
First torpedo entirely developed by Newport Station. It appears to have been of heavier construction than previous torpedoes.
| Ship Class Used On | Destroyers and Cruisers |
|---|---|
| Date Of Design | about 1927 |
| Date In Service | 1928 |
| Weight | 3,505 lbs. (1,590 kg) |
| Overall Length | 271 in (6.883 m) |
| Explosive Charge | 500 lbs. (227 kg) TNT |
| Range / Speed | 7,000 yards (6,400 m) / 44 knots
10,000 yards (9,150 m) / 34.5 knots 15,000 yards (13,700 m) / 27.5 knots |
| Power | Wet-heater |
A modified Mark 11 with the only difference being a reduction in the high speed setting to improve reliability. Approximately 100 manufactured.
"Torpedo: The Complete History of the World's Most Revolutionary Naval Weapon" by Roger Branfill-Cook
"Naval Weapons of World War Two" by John Campbell
"US Naval Weapons" and "US Submarines through 1945: An Illustrated Design History" both by Norman Friedman
"Ship Killers: A History of the American Torpedo" by Thomas Wildenberg and Norman Polmar
"A Brief History of U.S. Navy Torpedo Development"
Naval Undersea Museum
---
Letter to the Secretary of State from the (Acting) Secretary of the Navy, Admiral William Harrison Standley,
regarding export torpedoes for Brazil, dated 15 July 1936
---
Special help from Tom Apple and Alec Whalen
28 August 2008 - Benchmark
12 January 2009 - Added information on aircraft use of the Mark 7 torpedoes, added pictures of Virginia class battleship and Whitehead torpedo
26 June 2010 - Added information on Mark 8 torpedoes supplied to Britain and corrected typographical errors
18 December 2010 - Updated data tables to include guidance systems and other information
10 November 2014 - Added additional information
05 October 2019 - Converted to HTML 5 format
13 December 2023 - Added details on the Mark 8 Mod 3C and Mark 8 Mod 3E torpedoes.
13 August 2024 - Added Mark 8 use by PT Boats